The landscape of personal healthcare is undergoing a remarkable transformation, with health wearables leading the charge. These sophisticated devices have evolved from simple step counters to comprehensive health monitoring systems that track everything from heart rhythms to sleep quality. As technology advances, these wearable health devices are becoming increasingly accurate, affordable, and accessible to the average consumer.
Today’s health wearables offer unprecedented insights into our bodies, enabling us to take control of our wellbeing like never before. By providing real-time biometric monitoring and actionable data, these devices are empowering users to make informed decisions about their health before problems arise – truly revolutionizing proactive health management.
Modern health wearables offer comprehensive biometric monitoring capabilities
The Evolution of Health Wearables
The journey of health wearables began with basic pedometers and heart rate monitors. These early devices provided limited data and required manual tracking. Today’s health wearables represent a quantum leap in both capability and convenience, offering continuous monitoring of multiple health parameters simultaneously.
From Basic Trackers to Advanced Monitors
The first generation of fitness trackers primarily counted steps and estimated calories burned. Modern health wearables now incorporate multiple sensors that monitor heart rate, blood oxygen levels, skin temperature, sleep patterns, and even electrocardiogram (ECG) readings. This evolution has transformed these devices from simple fitness tools into comprehensive health monitoring systems.
Companies like Apple, Fitbit, and Garmin have pioneered advancements in sensor technology, making it possible to track increasingly complex biometric data with remarkable accuracy. The integration of artificial intelligence has further enhanced these capabilities, enabling devices to identify patterns and provide personalized insights.

The evolution from basic pedometers to advanced health wearables
Key Technological Advancements
Improved Sensor Accuracy
Modern photoplethysmography (PPG) sensors can detect minute changes in blood flow, enabling precise heart rate monitoring. Advanced accelerometers and gyroscopes track movement with greater accuracy, while electrodermal activity sensors measure stress levels through skin conductance.
Battery Efficiency
Significant improvements in battery technology and power management have extended the operational life of health wearables. Many devices now function for days or even weeks on a single charge, making continuous health monitoring practical for everyday use.
Data Processing Capabilities
On-device processing has become increasingly sophisticated, allowing for real-time analysis of biometric data. Cloud connectivity enables more complex processing and the integration of artificial intelligence for deeper insights and pattern recognition.
Stay Ahead of Health Technology Trends
Subscribe to our newsletter for the latest updates on health wearables and proactive health management strategies delivered directly to your inbox.
Key Benefits of Health Wearables for Proactive Health Management
Health wearables are transforming how we approach personal wellness by shifting the focus from reactive treatment to proactive management. These devices provide continuous monitoring and real-time feedback, enabling users to make informed decisions about their health before problems escalate.

Health wearables provide actionable insights through smartphone applications
Early Detection of Health Issues
One of the most significant advantages of health wearables is their ability to detect subtle changes in vital signs that might indicate developing health problems. For example, irregular heart rhythms detected by ECG-capable smartwatches have alerted users to potential cardiac issues before they experienced symptoms, allowing for timely medical intervention.
Continuous glucose monitors have revolutionized diabetes management by providing real-time blood sugar data, helping users avoid dangerous highs and lows. Some advanced wearables can even detect changes in respiratory patterns that might signal sleep apnea or other breathing disorders.
Personalized Fitness and Wellness Plans
By collecting data on activity levels, heart rate responses, recovery times, and sleep quality, health wearables enable the creation of highly personalized fitness plans. These devices can determine optimal workout intensities based on individual heart rate zones and recovery status, helping users maximize results while minimizing injury risk.
Many wearables now incorporate AI algorithms that analyze patterns in user data to provide tailored recommendations. These might include suggestions for optimal workout times based on circadian rhythms or personalized recovery protocols based on sleep quality and physical exertion.
Mental Health and Stress Management
Modern health wearables don’t just track physical metrics – many now monitor indicators of mental wellbeing as well. Devices equipped with electrodermal activity sensors can detect stress responses through changes in skin conductance, while heart rate variability measurements provide insights into autonomic nervous system function and stress resilience.
Some wearables offer guided breathing exercises and meditation sessions based on real-time stress levels, helping users manage anxiety and improve mental health. Sleep tracking features provide detailed analysis of sleep quality and patterns, enabling users to optimize their rest and recovery.
“Health wearables have transformed patient care by providing continuous, real-time data that was previously unavailable outside clinical settings. This technology empowers both patients and healthcare providers to make more informed decisions.”
Types of Health Wearables and Their Applications
The market for health wearables has expanded dramatically, with devices now available for monitoring various aspects of health and wellness. Each type of wearable offers unique capabilities designed to address specific health management needs.

Various types of health wearables serve different monitoring purposes
Fitness Trackers and Smartwatches
Fitness trackers and smartwatches represent the most common and versatile health wearables. These wrist-worn devices typically monitor activity levels, heart rate, sleep patterns, and increasingly, more advanced health metrics like blood oxygen saturation and ECG readings.
| Feature | Basic Fitness Tracker | Advanced Smartwatch |
| Step Counting | Yes | Yes |
| Heart Rate Monitoring | Basic (resting/active) | Continuous with arrhythmia detection |
| Sleep Tracking | Basic (duration) | Advanced (sleep stages, breathing) |
| Blood Oxygen | No | Yes |
| ECG Capability | No | Yes (medical-grade) |
| Stress Monitoring | Limited | Yes (HRV-based) |
Specialized Health Monitors
Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGMs)
CGMs have revolutionized diabetes management by providing real-time blood glucose data without the need for frequent finger pricks. These devices typically consist of a small sensor inserted under the skin that measures glucose levels in interstitial fluid. The data is transmitted to a smartphone app, allowing users to track trends and receive alerts for high or low glucose levels.
Smart Rings
Smart rings offer health tracking in a discreet, comfortable form factor. Devices like the Oura Ring monitor sleep quality, activity levels, and body temperature. Their small size makes them ideal for 24/7 wear, enabling continuous health monitoring without the bulk of a wrist-worn device.
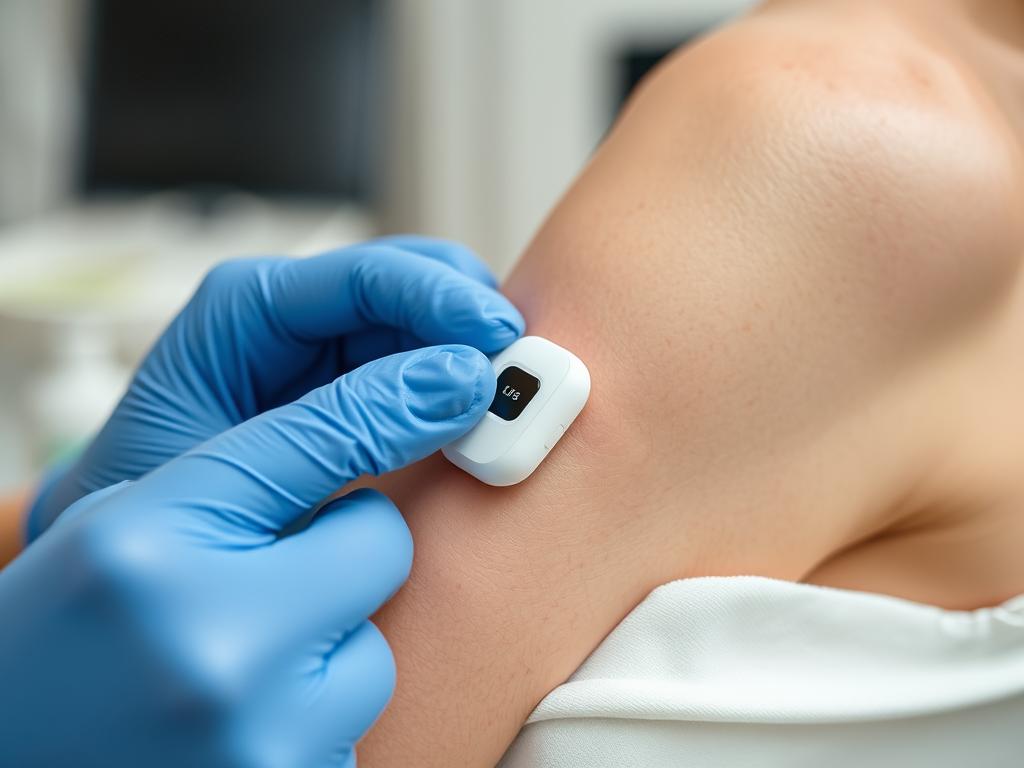
Continuous glucose monitors provide real-time blood sugar data
ECG/Heart Monitors
Dedicated ECG monitors provide medical-grade heart rhythm analysis. These devices can detect arrhythmias and other cardiac abnormalities, making them valuable tools for monitoring heart health, especially for those with known cardiac conditions. Some are designed for continuous wear, while others are used for periodic checks.
Blood Pressure Wearables
Emerging wearable technology now enables continuous or frequent blood pressure monitoring without the traditional cuff. These devices use various technologies, including pulse transit time and optical sensors, to estimate blood pressure throughout the day, providing a more comprehensive picture than occasional readings.
Discover the Latest in Health Monitoring Technology
Join our community to receive expert reviews, comparison guides, and exclusive content about cutting-edge health wearables.
Integration with Healthcare Systems
The true potential of health wearables is realized when their data is integrated into broader healthcare systems. This integration enables more comprehensive health monitoring and facilitates collaboration between patients and healthcare providers.
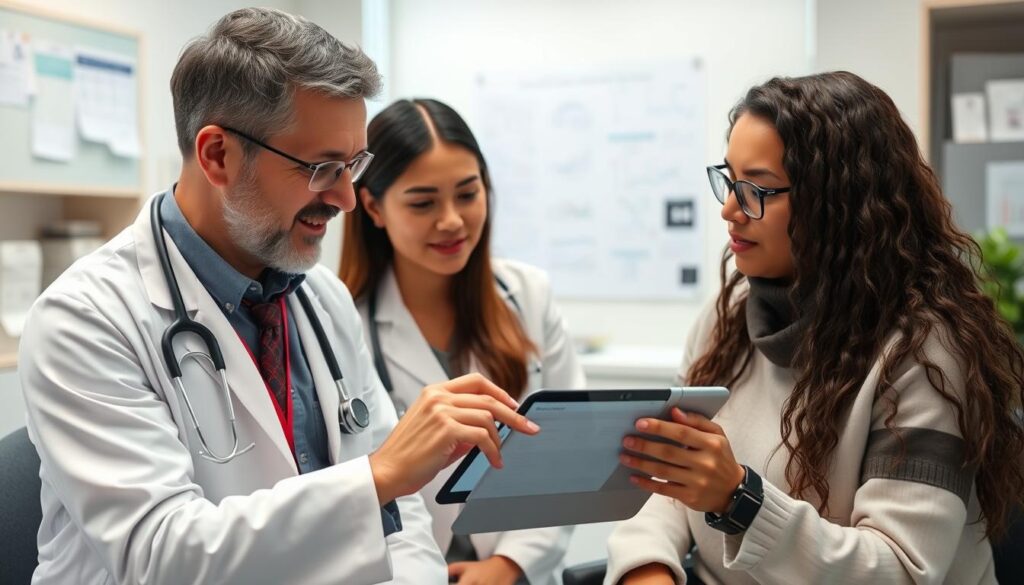

Health wearable data enhances doctor-patient consultations
Remote Patient Monitoring
Health wearables have become essential tools for remote patient monitoring, allowing healthcare providers to track patients’ vital signs and health metrics without requiring in-person visits. This capability is particularly valuable for managing chronic conditions like heart disease, diabetes, and hypertension.
Remote monitoring systems typically collect data from wearable devices, analyze it for concerning patterns, and alert healthcare providers when intervention may be necessary. This approach enables more proactive care, potentially preventing complications and reducing hospitalizations.
Electronic Health Records Integration
The integration of wearable data with electronic health records (EHRs) creates a more complete picture of patient health. When properly implemented, this integration allows healthcare providers to view long-term trends in patient metrics alongside traditional clinical data, enabling more informed treatment decisions.
Several major EHR platforms now offer interfaces for importing data from popular health wearables, though challenges remain in standardizing data formats and ensuring privacy and security compliance.
Privacy Consideration: When sharing health wearable data with healthcare providers, it’s important to understand how your information will be used and protected. Most reputable healthcare systems have strict privacy policies in place, but it’s always wise to ask questions about data security and sharing practices.
AI and Machine Learning in Health Wearables
Artificial intelligence and machine learning are transforming health wearables from simple tracking devices into intelligent health companions. These technologies enable devices to analyze complex patterns in biometric data and provide personalized insights and recommendations.

AI algorithms transform raw biometric data into actionable health insights
Predictive Health Analytics
One of the most promising applications of AI in health wearables is predictive analytics. By analyzing patterns in biometric data, AI algorithms can identify potential health issues before obvious symptoms appear. For example, subtle changes in heart rate variability, activity levels, and sleep patterns might indicate an oncoming illness days before the user feels sick.
Some advanced systems can even predict specific events like asthma attacks or epileptic seizures based on biometric precursors, potentially allowing for preventive intervention. As these algorithms continue to improve through machine learning, their predictive capabilities will become increasingly accurate and valuable.
Personalized Health Recommendations
AI enables health wearables to provide highly personalized recommendations based on individual data patterns. Rather than generic health advice, users receive suggestions tailored to their specific needs, preferences, and health status.
These recommendations might include optimal workout times based on circadian rhythms, personalized stress management techniques based on individual stress triggers, or dietary suggestions based on glucose response patterns. The more data the AI system has to analyze, the more personalized and effective these recommendations become.
How accurate are AI-powered health predictions from wearables?
The accuracy of AI-powered health predictions varies depending on the specific condition being monitored and the quality of the wearable’s sensors. For some applications, like detecting atrial fibrillation, advanced smartwatches have shown accuracy rates comparable to medical devices in clinical studies. However, for more complex predictions, the technology is still evolving.
It’s important to remember that while health wearables can provide valuable insights, they should complement rather than replace professional medical care. Always consult healthcare providers about significant health concerns, regardless of what your wearable device indicates.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite their tremendous potential, health wearables face several challenges that must be addressed to maximize their benefits for proactive health management.

Privacy and data security remain important considerations for health wearable users
Advantages
- Continuous health monitoring without clinical visits
- Early detection of potential health issues
- Personalized health insights and recommendations
- Improved engagement with personal health management
- Enhanced communication with healthcare providers
Challenges
- Data privacy and security concerns
- Accuracy limitations in some measurements
- Potential for information overload or anxiety
- Accessibility issues for certain populations
- Integration challenges with healthcare systems
Data Privacy and Security
Health wearables collect highly sensitive personal data, raising important privacy and security concerns. Users must trust that their biometric information will be protected from unauthorized access and used responsibly by device manufacturers and third-party applications.
When choosing a health wearable, it’s important to review the manufacturer’s privacy policy and understand what data is collected, how it’s stored, and with whom it might be shared. Look for devices that offer strong encryption, transparent data practices, and user control over information sharing.
Accuracy and Reliability
While health wearables have become increasingly accurate, they still have limitations. Factors like device placement, skin tone, tattoos, and movement can affect sensor readings. Users should understand these limitations and interpret their data accordingly.
For critical health monitoring, medical-grade devices with FDA clearance or approval offer greater reliability. However, even consumer-grade wearables can provide valuable insights when their limitations are properly understood.
Make Informed Decisions About Health Technology
Subscribe to receive our comprehensive guides on choosing and using health wearables effectively, including privacy protection strategies and accuracy considerations.
Future Trends in Health Wearables
The field of health wearables continues to evolve rapidly, with several exciting developments on the horizon that promise to further enhance their capabilities for proactive health management.

Next-generation health wearables will feature advanced sensing capabilities and form factors
Emerging Technologies
Non-Invasive Glucose Monitoring
Several companies are working on non-invasive glucose monitoring technologies that would eliminate the need for sensor insertion or finger pricks. These approaches use various methods, including optical sensing and microwave technology, to measure blood glucose levels through the skin.
If successful, this technology would dramatically improve diabetes management and could also provide valuable metabolic insights for non-diabetic users interested in optimizing their nutrition and energy levels.
Smart Clothing and Textiles
Smart textiles with embedded sensors offer a promising alternative to traditional wearable devices. These garments can monitor various health metrics while providing the comfort and convenience of regular clothing.
Applications include smart shirts that monitor cardiac function, compression garments that track muscle activity and recovery, and smart socks that detect foot pressure abnormalities for diabetic patients at risk of foot ulcers.
Advanced Biomarker Detection
Future wearables may be able to detect a wider range of biomarkers through non-invasive means. Sweat analysis, for example, can potentially provide insights into hydration status, electrolyte balance, and even stress hormone levels.
Some researchers are developing wearable patches that can analyze interstitial fluid for various biomarkers, potentially offering a window into internal biochemistry without breaking the skin.
Integration with Broader Health Ecosystems
The future of health wearables lies not just in improved sensors and algorithms but also in better integration with broader health ecosystems. This includes seamless connectivity with healthcare providers, integration with smart home systems for holistic health monitoring, and interoperability between different health devices and platforms.
As standards for health data exchange continue to develop, users will benefit from more comprehensive health insights drawn from multiple data sources, creating a more complete picture of their overall wellbeing.

Future health wearables will integrate seamlessly with comprehensive health ecosystems
Getting Started with Health Wearables
With so many options available, choosing and using health wearables effectively can seem overwhelming. Here are some practical tips for getting started with these powerful health management tools.

Setting up a health wearable typically involves pairing with a smartphone app
Choosing the Right Device
When selecting a health wearable, consider your specific health goals and monitoring needs. Are you primarily interested in fitness tracking, sleep analysis, heart health monitoring, or managing a specific condition like diabetes? Different devices excel in different areas, so prioritize features that align with your personal health objectives.
Also consider practical factors like battery life, water resistance, comfort, and compatibility with your smartphone or other devices. Reading expert reviews and user experiences can provide valuable insights into real-world performance and reliability.
Maximizing Value from Your Health Wearable
Establish a Baseline
When you first start using a health wearable, focus on establishing your personal baselines for various metrics. Everyone’s “normal” is different, and understanding your typical patterns is essential for identifying meaningful changes over time.
Set Realistic Goals
Use your wearable to set and track progress toward realistic health goals. Whether it’s increasing daily activity, improving sleep quality, or managing stress more effectively, concrete objectives help you make the most of your device’s capabilities.
Share Data Thoughtfully
Consider sharing relevant health data with your healthcare providers. Many doctors now welcome this additional information, especially for managing chronic conditions. However, focus on sharing meaningful patterns rather than overwhelming them with raw data.

Regular review of health metrics helps identify meaningful patterns
Tip: Most health wearables provide the most value when worn consistently. Try to incorporate your device into your daily routine so that you collect continuous data, which provides more meaningful insights than sporadic measurements.
Conclusion: The Future of Proactive Health Management
Health wearables represent a fundamental shift in how we approach personal wellness, moving from reactive healthcare to proactive health management. By providing continuous biometric monitoring and actionable insights, these devices empower users to make informed decisions about their health before problems arise.
As sensor technology, artificial intelligence, and data analytics continue to advance, health wearables will become even more powerful tools for understanding and optimizing our wellbeing. Integration with broader healthcare systems will further enhance their value, creating a more connected and personalized approach to health management.
Whether you’re managing a chronic condition, working toward specific fitness goals, or simply interested in better understanding your body, health wearables offer unprecedented insights into your personal health metrics. By embracing these technologies thoughtfully and using them as part of a comprehensive approach to wellness, you can take control of your health journey in ways that were impossible just a few years ago.

Health wearables support active lifestyles through continuous monitoring and personalized insights
Transform Your Approach to Health Management
Subscribe to our newsletter for regular updates on the latest health wearable technologies, expert tips for maximizing their benefits, and exclusive guides to proactive health management.