Did you know that 60% of Americans live with chronic inflammatory conditions? These conditions, like obesity, diabetes, and heart disease, are often linked to systemic inflammation. The good news? Your food choices can play a powerful role in reducing this inflammation.
Eating the right foods can help lower inflammation markers in your body. For example, the Mediterranean diet is often praised as a gold standard for healthy eating. It’s packed with foods that naturally fight inflammation, like fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats.
In this article, we’ll explore the science behind anti-inflammatory diets, share a list of the best foods to include, and provide tips for meal planning and cooking. Ready to take control of your health? Let’s dive in!
What Are Anti-Inflammatory Diets?
Chronic inflammation is a growing concern for many Americans, but the right eating habits can make a difference. An anti-inflammatory diet isn’t a strict regimen but a flexible eating pattern. It focuses on foods that naturally reduce inflammation and promote overall health.
This approach emphasizes omega-3 fatty acids, colorful produce, and healthy fats. Unlike the standard American diet, which is high in processed foods, it prioritizes whole, nutrient-dense ingredients. Research from Johns Hopkins highlights the effectiveness of the Mediterranean diet in reducing inflammation and preventing chronic diseases.

Key components of this eating pattern include fatty fish, nuts, berries, leafy greens, and olive oil. These foods are rich in antioxidants and polyphenols, which help combat inflammation. By incorporating more whole grains and fruits vegetables, you can create meals that are both delicious and beneficial for your health.
| Anti-Inflammatory Foods | Processed Foods |
|---|---|
| Fatty fish (salmon, mackerel) | Fried foods |
| Leafy greens (spinach, kale) | Sugary snacks |
| Whole grains (quinoa, brown rice) | Refined grains (white bread) |
| Berries (blueberries, strawberries) | Processed meats |
Switching to an anti-inflammatory eating pattern doesn’t have to be overwhelming. Start by adding more fruits vegetables and healthy fats to your meals. Over time, these small changes can lead to significant improvements in your health.
The Science Behind Chronic Inflammation
Inflammation is your body’s natural defense mechanism, but when it becomes chronic, it can harm your health. Acute inflammation, like the redness around a healing bruise, is a short-term response to injury or infection. Chronic inflammation, however, is like a smoldering fireplace that never goes out—it quietly damages your body over time.
Two key biomarkers, C-reactive protein (CRP) and interleukin-6, are often used to measure inflammation levels. A CRP level above 3mg/L indicates a high risk of chronic inflammation. Research shows that chronic inflammation is linked to 7 out of 10 leading causes of death in the U.S., including heart disease, diabetes, and arthritis.
Here’s how chronic inflammation impacts your health:
- Heart disease: The #1 killer in the U.S., often fueled by prolonged inflammation.
- Diabetes: Inflammation can interfere with insulin sensitivity.
- Arthritis: Joint pain and stiffness are common symptoms.
- Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD): Chronic inflammation in the digestive tract.
A Harvard study found that following a Mediterranean-style eating pattern can reduce CRP levels by 28%. This highlights the importance of choosing foods that support your body’s natural balance. By understanding the science behind inflammation, you can take steps to protect your health and reduce your risk of chronic diseases.
Benefits of Anti-Inflammatory Diets
Adopting a nutrient-rich eating pattern can significantly improve your health and reduce inflammation. Studies show that this approach lowers the risk of chronic diseases like heart disease, arthritis, and even cognitive decline. By focusing on whole, unprocessed foods, you can support your body’s natural defenses and enhance overall well-being.

Reducing the Risk of Chronic Diseases
Research highlights the powerful impact of this eating pattern. The PREDIMED study found a 30% reduction in cardiovascular events among participants. Similarly, BMC trials reported a 23% decrease in arthritis pain. These results demonstrate how food choices can transform your health.
Here are some key benefits:
- Cardiovascular benefits: Improved cholesterol levels and blood pressure.
- Arthritis relief: Reduced joint swelling and stiffness.
- Cognitive protection: A 35% lower risk of Alzheimer’s, according to UCLA research.
- Gut health: Increased microbiome diversity with prebiotic-rich foods.
- Cancer prevention: Antioxidants protect against cell damage.
| Health Benefit | Impact |
|---|---|
| Heart Disease | 30% lower risk (PREDIMED) |
| Arthritis | 23% pain reduction (BMC) |
| Alzheimer’s | 35% lower risk (UCLA) |
| Gut Health | Improved microbiome diversity |
| Cancer | Antioxidant protection |
By incorporating these foods into your daily routine, you can reduce inflammation and protect your body from chronic diseases. Small changes can lead to big results, so start today!
Top Anti-Inflammatory Foods to Include
Certain foods can act as natural warriors against inflammation, helping your body stay healthy. By incorporating these nutrient-packed options into your meals, you can support your body’s ability to fight inflammation and improve overall well-being.
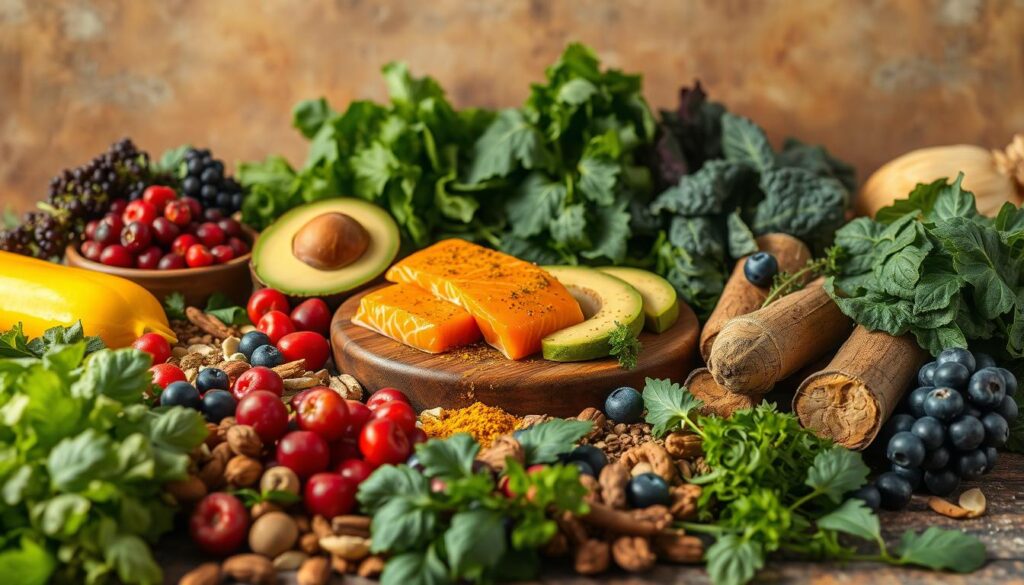

Omega-3 Fatty Acids: The Inflammation Fighter
Omega-3 fatty acids are essential for reducing inflammation. Fatty fish like salmon, tuna, and sardines are excellent sources, providing high levels of EPA and DHA. Just 3 ounces of salmon offers 1.8 grams of omega-3s, making it a top choice.
For plant-based options, consider chia seeds, Brussels sprouts, and walnuts. Walnuts, for example, contain 2.5 grams of omega-3s per ounce. These foods not only fight inflammation but also support heart and brain health.
Antioxidant-Rich Fruits and Vegetables
Colorful produce is packed with antioxidants that combat inflammation. Blueberries, cherries, and bell peppers are standout options. Blueberries provide 24% of the daily recommended intake of vitamin K, while bell peppers offer 95mg of vitamin C per serving.
Leafy greens like spinach and kale are also powerful allies. Spinach retains more nutrients when eaten raw, while kale is rich in quercetin, a potent antioxidant. Including these in your diet can help protect your cells from damage.
| Food | Key Nutrient | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Salmon | Omega-3 fatty acids | Reduces inflammation |
| Walnuts | Plant-based omega-3s | Supports brain health |
| Blueberries | Vitamin K | Protects cells |
| Spinach | Iron and antioxidants | Boosts immunity |
| Kale | Quercetin | Fights oxidative stress |
Adding these foods to your meals is simple and effective. Start with small changes, like swapping processed snacks for nuts or adding a handful of spinach to your smoothie. Over time, these choices can lead to a healthier, more vibrant you.
Foods to Avoid for Lower Inflammation
Many everyday foods can secretly fuel inflammation, harming your health over time. While some ingredients are obvious culprits, others hide in plain sight. Understanding what to avoid can help you make better choices and reduce inflammation naturally.

The Hidden Dangers of Added Sugars
Added sugars are one of the biggest contributors to inflammation. Shockingly, 74% of packaged foods contain added sugars, often under names like barley malt or dextrose. These sugars can spike blood sugar levels and trigger inflammatory responses in the body.
Here’s what to watch out for:
- Sugar aliases: Look for terms like high-fructose corn syrup, maltose, or sucrose on labels.
- Low-fat traps: Many “low-fat” products compensate with added sugars, making them worse for inflammation.
- Processed snacks: Cookies, sodas, and candies are packed with hidden sugars.
Processed Foods and Harmful Fats
Processed foods are another major culprit. They often contain unhealthy fats and additives that promote inflammation. Trans fats, though banned in many places, still lurk in some baked goods and fried foods. These fats can increase bad cholesterol and trigger inflammatory markers.
Fried foods are particularly harmful. High-heat cooking creates advanced glycation end-products (AGEs), which can damage cells and worsen inflammation. Acrylamide, a chemical formed in fried foods, is another concern.
| Foods to Avoid | Why They’re Harmful |
|---|---|
| Processed meats | Nitrates can lead to nitric oxide reactions, increasing inflammation. |
| Fried foods | High in AGEs and acrylamide, which damage cells. |
| Sugary snacks | Spike blood sugar and trigger inflammatory responses. |
| Refined grains | Lack fiber and nutrients, promoting inflammation. |
Alcohol is another factor to consider. While moderate consumption can be part of a healthy lifestyle, excessive drinking can increase inflammation. Experts recommend limiting alcohol to one drink per day for women and two for men.
By avoiding these foods and making smarter choices, you can reduce inflammation and support your overall health. Start by reading labels carefully and opting for whole, unprocessed ingredients whenever possible.
How to Start an Anti-Inflammatory Diet
Starting a healthier eating pattern doesn’t have to be overwhelming. By making simple swaps in your meals, you can gradually transition to a diet that supports your health. The key is to focus on small, sustainable changes rather than an overnight overhaul.

Simple Swaps for a Healthier Diet
One of the easiest ways to improve your diet is by replacing processed foods with nutrient-rich options. For example, swap white rice for cauliflower rice or pasta for zucchini noodles. These changes not only reduce inflammation but also add more vitamins and fiber to your meals.
Here are some practical ideas to get started:
- Pantry makeover: Replace canola oil with avocado oil for healthier fats.
- Flavor hacks: Use nutritional yeast instead of parmesan for a cheesy, nutrient-packed alternative.
- Snack transitions: Choose almonds over chips or dark chocolate over candy for a satisfying treat.
- Beverage shifts: Opt for a golden milk latte instead of sugary coffee drinks.
- Dining out: Select grilled fish tacos over fried chicken for a healthier meal.
| Swap This | For This |
|---|---|
| White rice | Cauliflower rice |
| Pasta | Zucchini noodles |
| Canola oil | Avocado oil |
| Parmesan | Nutritional yeast |
| Chips | Almonds |
By incorporating these swaps into your daily routine, you can create meals that are both delicious and beneficial. Remember, the goal is progress, not perfection. Start with one or two changes and build from there.
Meal Planning for Anti-Inflammatory Diets
Planning your meals can be a game-changer for managing inflammation and improving your health. A structured approach ensures you get the right balance of nutrients while keeping your meals exciting and varied. With a focus on whole, unprocessed foods, you can create a plan that supports your body’s natural defenses.
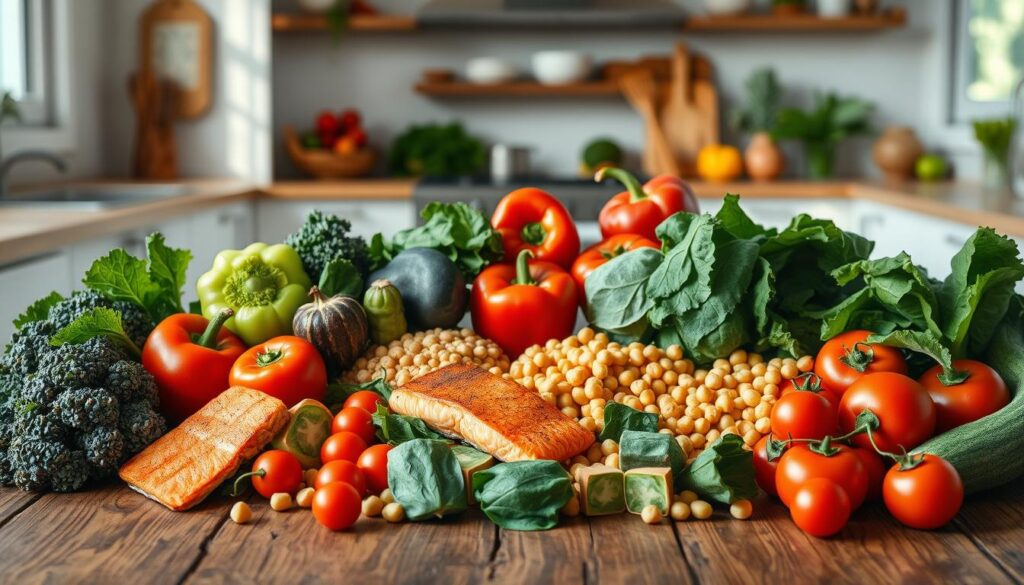

Sample Meal Plan for a Week
Here’s a 1,800-calorie meal plan packed with 30g of fiber to help you get started. Each meal is designed to include nutrient-dense ingredients like fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats. Try these ideas to keep your week flavorful and inflammation-free:
- Breakfast: Greek yogurt topped with raspberries and a sprinkle of flaxseed for a fiber-rich start.
- Lunch: Massaged kale salad with chickpeas, olive oil, and a squeeze of lemon for a refreshing midday boost.
- Dinner: Sheet-pan trout with roasted Brussels sprouts, drizzled with avocado oil for healthy fats.
- Snacks: Apple slices with almond butter or a handful of spiced nuts for a satisfying crunch.
For added convenience, consider batch-cooking soups or preparing overnight oats. These strategies save time while ensuring you have healthy options ready to go. Recipes like turmeric chia pudding and salmon Buddha bowls are perfect for incorporating anti-inflammatory ingredients into your routine.
By focusing on whole foods and smart prep techniques, you can make meal planning a seamless part of your lifestyle. Start small, experiment with recipes, and enjoy the benefits of a well-balanced, inflammation-fighting diet.
The Role of Cooking Methods in Reducing Inflammation
The way you cook your food can have a big impact on inflammation levels in your body. Certain cooking methods preserve nutrients better, while others can create harmful compounds. By choosing healthier techniques, you can reduce inflammation and support your overall health.

Healthier Alternatives to Frying and Grilling
Not all cooking techniques are created equal. For example, microwaving vegetables preserves more nutrients than boiling. Poaching fish helps maintain its omega-3 fatty acids, unlike frying, which can destroy them. Here are some tips to make your cooking healthier:
- Temperature guide: Cook below 375°F to prevent oxidation and preserve nutrients.
- Best oils: Use extra virgin olive oil with a smoke point of 410°F for sautéing and baking.
- Marinating tips: Lemon juice can reduce harmful compounds like AGEs by 50%.
- Safe grilling: Use cedar planks and trim fat drips to minimize harmful smoke.
- Steam-sauté technique: Replace oil with water or broth for a lighter, healthier option.
These small changes can make a big difference in reducing inflammation and improving your health. For example, using olive oil instead of butter adds healthy fats that fight inflammation. Similarly, steaming vegetables retains more vitamins than boiling.
| Cooking Method | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Microwaving | Preserves nutrients better than boiling |
| Poaching | Maintains omega-3s in fish |
| Steam-sauté | Uses water or broth instead of oil |
| Grilling with cedar planks | Reduces harmful smoke |
By adopting these healthier cooking methods, you can reduce inflammation and enjoy delicious, nutrient-packed meals. Start with one or two changes and gradually incorporate more into your routine.
How Anti-Inflammatory Diets Compare to Other Diets
When comparing eating patterns, the Mediterranean diet stands out for its focus on whole, nutrient-rich foods. This approach shares similarities with other diets but also has key differences that make it unique. Understanding these distinctions can help you choose the best plan for your health.
Similarities and Differences
The anti-inflammatory diet emphasizes quality carbs, healthy fats, and colorful produce. Unlike the Keto diet, which restricts carbs, it focuses on whole grains and fruits. This makes it more sustainable for long-term health. While Keto may help with weight loss, it often lacks the variety needed to fight inflammation effectively.
Compared to Vegan diets, the Mediterranean diet includes fish, a rich source of omega-3s. Vegan diets may miss these essential fats unless carefully planned. Similarly, Paleo diets exclude legumes, which are packed with anti-inflammatory benefits. This limits their ability to support overall health.
The DASH diet, designed to lower blood pressure, shares some elements with the anti-inflammatory diet. Both limit sodium and prioritize whole foods. However, DASH allows more dairy, which may not suit everyone. The MIND diet, focused on brain health, also overlaps with its emphasis on berries and leafy greens.
- Vs Keto: Emphasizes carb quality over quantity.
- Vs Vegan: Prioritizes fish over meat substitutes.
- Vs DASH: Both limit sodium, but DASH allows more dairy.
- Shared elements with MIND diet: Berry focus.
- Unique aspect: Specific polyphenol targeting.
By understanding these comparisons, you can tailor your eating plan to support your heart health and reduce the risk of chronic disease. Whether you choose the Mediterranean diet or another approach, the key is to focus on whole, nutrient-dense foods that fight inflammation naturally.
Long-Term Benefits of Anti-Inflammatory Diets
Consistent healthy eating habits can transform your health in the long run. A 5-year study shows a 62% adherence rate to this lifestyle, proving its sustainability. By following the 80/20 rule—allowing three “cheat meals” weekly—you can maintain balance without feeling restricted.
Sustaining Healthy Eating Habits
Adopting this approach offers numerous benefits, from reducing chronic inflammation to improving overall health. Here’s how you can make it work for you:
- Aging benefits: Studies show reduced cellular senescence markers, promoting longevity.
- Cost analysis: This eating pattern is $2.50/day cheaper than the standard diet, making it budget-friendly.
- Travel tips: Pack smoked salmon and individual nut packs for on-the-go nutrition.
- Family adaptation: Kid-friendly options like sweet potato fries make it easier to involve everyone.
- Tech tools: Use apps like Cronometer to track nutrients and stay on course.
Incorporating more fiber-rich foods like vegetables and whole grains can improve digestion and reduce inflammation. Healthy fats, such as those found in almonds and olive oil, support heart health and provide sustained energy.
| Benefit | Impact |
|---|---|
| Reduced Inflammation | Lower markers of chronic inflammation |
| Cost Savings | $2.50/day cheaper than standard diets |
| Family-Friendly | Easy to adapt for kids |
| Travel Convenience | Portable, nutrient-dense snacks |
| Tech Support | Apps for tracking nutrients |
By focusing on these strategies, you can enjoy the long-term benefits of a healthier lifestyle. Start small, stay consistent, and watch your health improve over time.
Conclusion
Making small changes to your daily meals can have a lasting impact on your health. Start by adding two fish meals a week and filling your plate with a rainbow of produce. These simple steps can help reduce inflammation and support your body’s natural defenses.
Take inspiration from Sarah, who saw her arthritis pain drop by 40% after adopting these habits. Her story shows that consistency matters more than perfection. Small, steady changes can lead to big results over time.
Ready to take the next step? Download our free 7-day meal plan PDF to kickstart your journey toward healthy eating. Remember, your fork is your best tool for fighting chronic diseases and staying vibrant.
